
Understanding Pneumonia in Children: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment

Autor - Dr. Amit Gupta
MD (peds) KGMC LUCKNOW, PGPN (Boston), NNF Instructor, Fellowship in Neonatology (Canada )
Senior Consultant - Peadiatrician & Neonatologist
Understanding Pneumonia in Children: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction:
Pneumonia is a common respiratory infection that can affect people of all ages, but it can be particularly concerning when it strikes children. As a seasoned child specialist with 18 years of experience, I aim to provide you with a comprehensive educational article on pneumonia, covering its causes, symptoms, and treatment, to help parents and caregivers better understand this condition and its management.
What Is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs caused by various infectious agents, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms. In children, bacterial and viral pneumonia are the most common culprits. Pneumonia can range from mild to severe, and it is crucial to recognize its signs and symptoms to ensure timely intervention and proper treatment.
Causes of Pneumonia in Children:
Bacterial Infections: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae type b, and Staphylococcus aureus are some common bacterial pathogens responsible for pediatric pneumonia.
Viral Infections: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), influenza virus, and adenovirus are frequent viral causes of pneumonia in children.
Fungal Infections: While less common, fungal pneumonia can occur, primarily in children with compromised immune systems.
Symptoms of Pneumonia in Children:
Recognizing the symptoms of pneumonia in children is essential for early diagnosis and prompt treatment. These symptoms may vary in severity and can include:
- Cough, often producing yellow or green mucus.
- High fever, sometimes accompanied by chills.
- Rapid or difficult breathing, which may be visible as chest retractions (sucking in between the ribs or below the ribcage) or flaring of the nostrils.
- Wheezing or grunting.
- Fatigue and decreased activity.
- Loss of appetite.
- Rapid heart rate.
- Cyanosis (bluish discoloration of the lips, nails, or skin).
- Diagnosis of Pneumonia:
When a child presents with symptoms suggestive of pneumonia, a thorough evaluation is necessary. Diagnostic measures may include:
Physical examination: Listening to the child's breathing sounds with a stethoscope to identify abnormal breath sounds, crackles, or wheezing.
Chest X-ray: An essential tool for confirming the presence of pneumonia and determining its extent.
Blood tests: To assess the severity of infection and the type of pathogen involved.
Sputum culture: To identify the causative bacteria and guide antibiotic treatment.
Treatment of Pneumonia in Children:
The treatment approach for pediatric pneumonia depends on the underlying cause and the child's age and overall health. Key strategies include:
Antibiotics: If bacterial pneumonia is diagnosed, antibiotics are prescribed. The choice of antibiotic depends on the suspected pathogen.
Antiviral medications: For pneumonia caused by specific viruses, such as influenza or RSV, antiviral drugs may be considered.
Supportive care: This includes ensuring the child gets plenty of rest, maintaining hydration, and managing fever and discomfort with appropriate medications.
Oxygen therapy: In severe cases, oxygen supplementation may be required to ensure adequate oxygen levels in the blood.
Hospitalization: Some children with pneumonia, especially infants or those with severe symptoms, may require hospitalization for close monitoring and intravenous treatments.
Prevention of Pneumonia:
Preventing pneumonia in children is a priority for parents and caregivers. Here are some essential preventive measures:
Vaccination: Ensure that your child is up-to-date on vaccinations, including those against common pathogens like pneumococcus and Hib.
Good hygiene: Promote handwashing and respiratory hygiene to reduce the spread of infectious agents.
Avoid secondhand smoke: Exposure to tobacco smoke can increase the risk of pneumonia.
Breastfeeding: Breastfed infants have better immunity against infections, including pneumonia.
Conclusion:
As a child specialist, I understand the concern and worry that parents and caregivers may experience when a child is diagnosed with pneumonia. Early recognition of symptoms, prompt medical attention, and appropriate treatment can significantly improve the outcome for children with pneumonia. By focusing on prevention and staying informed, we can work together to keep our children healthy and safe.
Related Blogs

Understanding Gestational Diabetes: Insights from Dr Shruthi Kalagara
Read More
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Pregnancy
Read More
Early Pregnancy Care for New Pregnant Women: Expert Advice | Motherhood Hospitals
Read More
Body Positivity Tips Post C Section (Cesarean Delivery)
Read More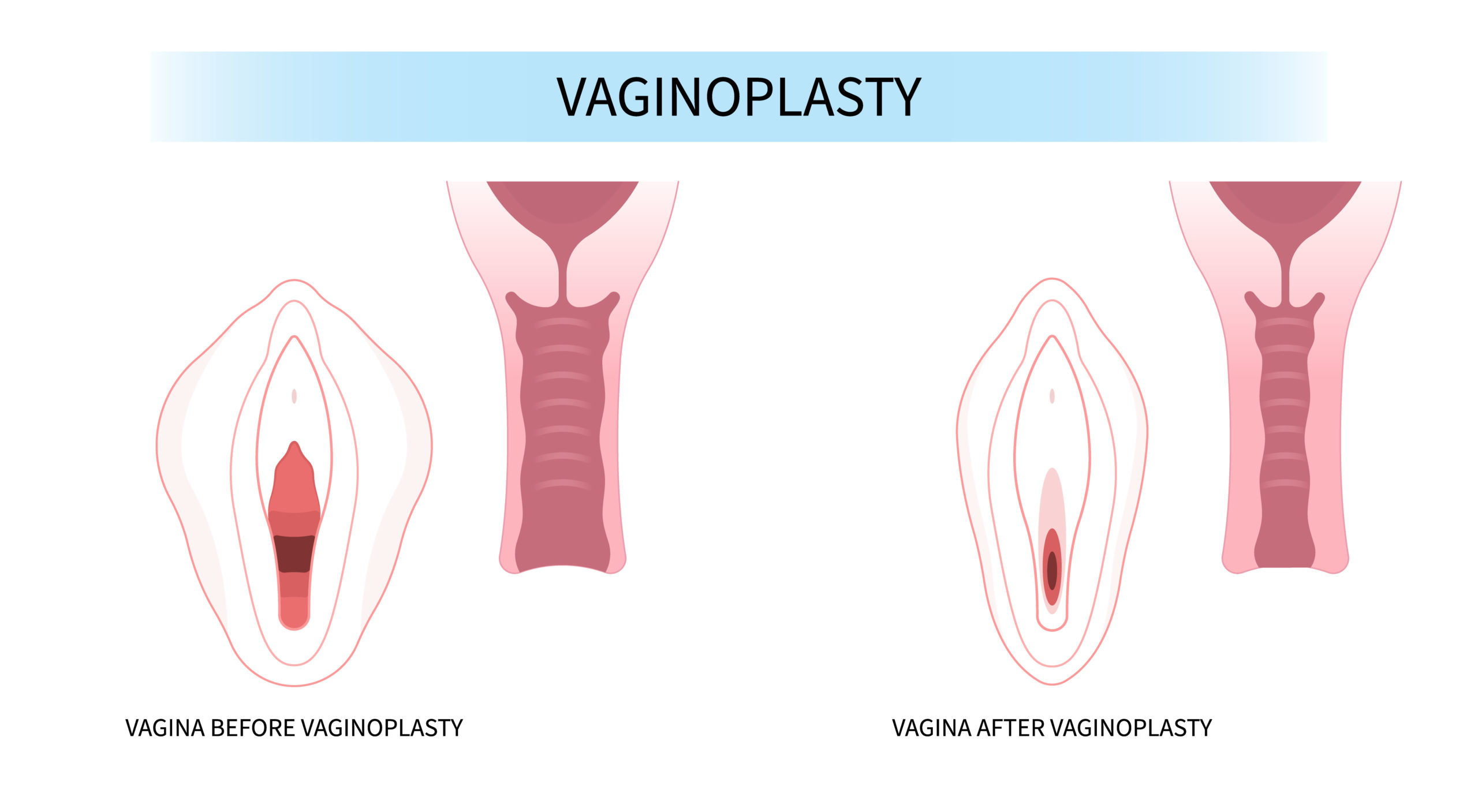
Vaginoplasty: Procedure, Cost, Risks & Benefits, Recovery
Read More
The Digital Dilemma: Exploring the Medical Implications of Technology on Child Development
Read More
How To Relieve Menstrual Cramps? - 8 Simple Tips
Read More
Benefits of Consuming Folic Acid Tablets For Pregnancy/During Pregnancy
Read More
Navigating Radiology: Ensuring Safe Imaging During Pregnancy
Read More
Navigating Radiological Tests During Pregnancy: Ensuring Safety for Mother and Child
Read MoreRequest A Call Back
Leave a Comment:
View Comments
Previous
Next
HELLO,
Stay update don our latest packages, offer, news, new launches, and more. Enter your email to subscribe to our news letter


 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number






No comment yet, add your voice below!