
Multiple Pregnancy

Multiple pregnancy is when there are more than one embryo getting attached to uterine lining and developing into multiple foetuses. This can be twins, triplets, quadruplets or higher order pregnancies. The incidence of twins is gone up from 18.9/1000 live births in 1980 to 32.1/1000 live births.
How multiple pregnancy happens?
One baby growing in the womb (uterus) on its own is called a singleton pregnancy. By far the most common type of multiple pregnancy is a twin pregnancy when there are two babies. Having three babies in the same pregnancy is known as triplets and having four is known as quadruplets. It is very rare to have more than four. Multiple pregnancy happens because two to three eggs get fertilized with two to three sperms or when one fertilised egg make two to three instead of one embryo.
Let us understand about TWINS as this is the commonest of all multiple pregnancies. Also, it is important to understand that the placenta is crucial to the pregnancy - it is the place where your body 'meets' your baby directly to pass across the nutrients your baby needs to grow. When an egg is fertilized it starts dividing till it convert itself into a zygote. If split occurs in early stage of cell division identical twins are formed. This cell division continues until it converts into a ball of cells and starts implanting itself in the lining of womb and becomes an embryo. The cells will form distinct areas like central group forms the baby and outer lining form the amniotic sac.
Types of twins:
- Dichorionic diamniotic (DCDA): Two placenta and two amniotic sacs.
- Mono chorionic diamniotic (MCDA): One placenta and two sacs.
- Mono chorionic mono amniotic (MCMA): One placenta and one sac
- Maternal age: women more than 35 are more prone to conceive multiple.
- Fertility medication: These drugs stimulate ovaries to produce multiple eggs
- Family history: History of multiple gestation in the family makes one prone for the same.
- Had a history of twin in the past.
- premature birth
- low birth weight
- Twin to twin transfusion
- Discordant growth
- Miscarriages
- Gestational diabetes
- Preeclampsia or hypertension
- Severe hyperemesis
- Foetal reduction: this is termination of one or more foetuses after the NT USG . Proper understanding of the procedure from parental side is very important. Risk of abortion needs special attention.
- More frequent visits to obstetrician
- Cervical encircalage / stitch: It's role in preventing miscarriage is doubtful
- Vaginal progesterone: this is known to help keep cervical integrity
- Dietician advice to help prevent GDM
- Ecosprin can be advised for prevention of preeclampsia
- More frequent scans to understand the growth pattern.
- Intervention by foetal Medicine expert if required
- Vigilant postnatal care as the chances of post-natal depression is high
- Avoid alcohol, smoking as advised with any singleton pregnancy.
- Steroid injection: these injections are given to mother to help the maturity of foetal lungs, by doing this we can avoid/ decrease the stay of babies in NICU
- The babies are growing properly
- Position of babies in the womb normal and conducive for normal delivery
- MCMA twins
- Pprom: water break/ leaking prematurely before term
- Unfavourable position
- CPD wherein the birth passage is narrow
- Second twin after vaginal birth of first baby, if vaginal delivery not possible due to abnormal lie and position of baby, decreasing heart rate, placental abruption
Related Blogs

Understanding Gestational Diabetes: Insights from Dr Shruthi Kalagara
Read More
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Pregnancy
Read More
Early Pregnancy Care for New Pregnant Women: Expert Advice | Motherhood Hospitals
Read More
Body Positivity Tips Post C Section (Cesarean Delivery)
Read More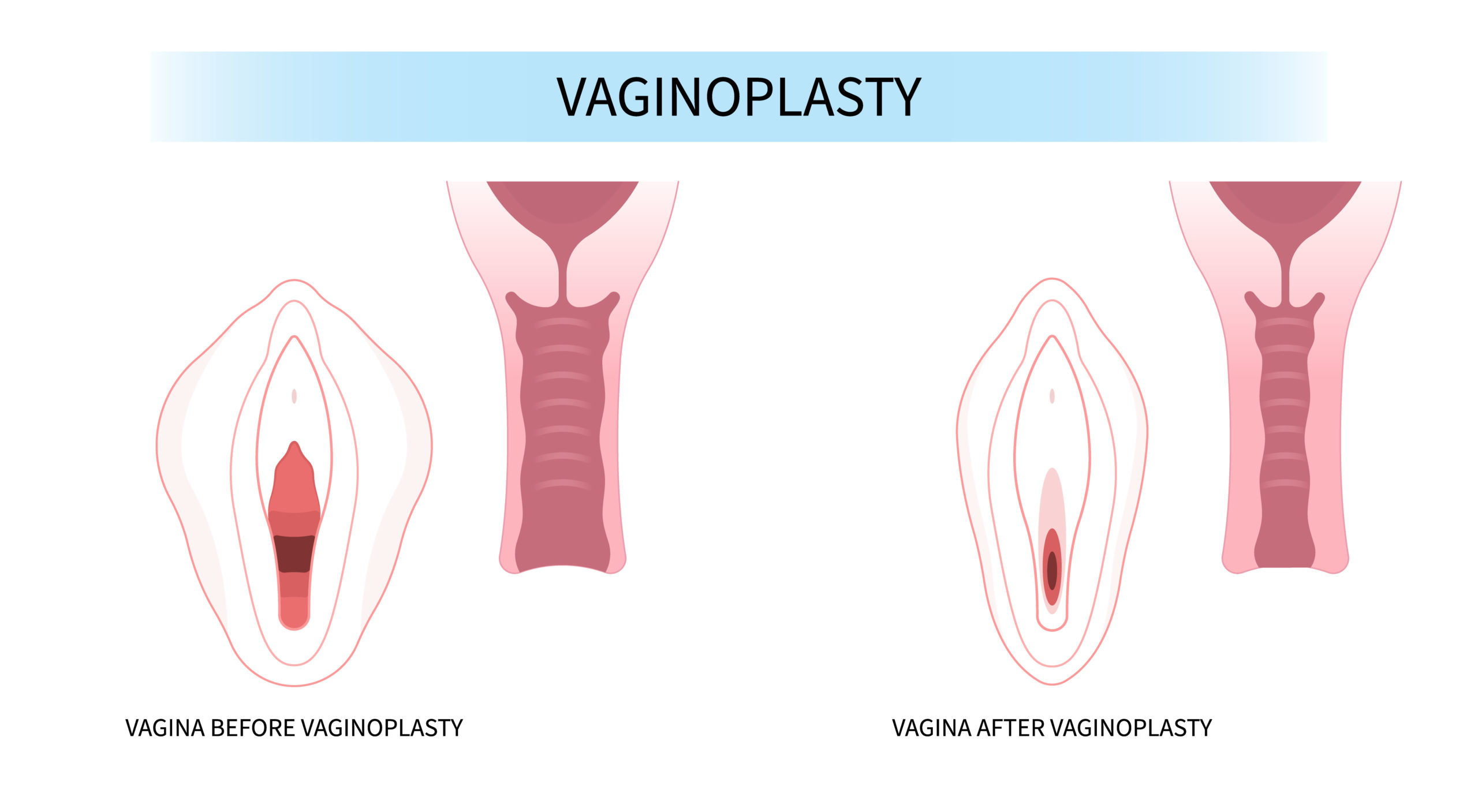
Vaginoplasty: Procedure, Cost, Risks & Benefits, Recovery
Read More
The Digital Dilemma: Exploring the Medical Implications of Technology on Child Development
Read More
How To Relieve Menstrual Cramps? - 8 Simple Tips
Read More
Benefits of Consuming Folic Acid Tablets For Pregnancy/During Pregnancy
Read More
Navigating Radiology: Ensuring Safe Imaging During Pregnancy
Read More
Navigating Radiological Tests During Pregnancy: Ensuring Safety for Mother and Child
Read MoreRequest A Call Back
Leave a Comment:
View Comments
Previous
Next
HELLO,
Stay update don our latest packages, offer, news, new launches, and more. Enter your email to subscribe to our news letter


 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number






No comment yet, add your voice below!