Author – Dr Monika Chhajed, MBBS
Consultant – Paediatric Neurologist at Motherhood Chaitanya Hospital, Chandigarh
Emergency Management of Seizures in Children
Epilepsy in children can be challenging to treat. As a parent, you must be worried about controlling the seizures in your children. According to Dr Monika Chhajed, MBBS, Fellowship Paediatric Neurology and Epilepsy, DCH, DNB, Consultant-Paediatric Neurologist, the annual incidence of epilepsy in children is reported as 10 to 73 episodes/100,000 children. It is the highest in children younger than 2 years of age. If your child is suffering from epilepsy, you must know the emergency management of seizures.
What is Epilepsy?
According to the best paediatrician & neonatologist in Chandigarh, epilepsy is defined as a sudden activity of the brain with loss of consciousness for longer than 30 minutes.
Emergency Management of Seizures in Children
The best neonatologist doctor in Chandigarh tells us that there is no “gold standard” for the management of epilepsy in children. The treatment is provided with a combination of therapies. Being a parent to a child suffering from epilepsy, however, you should know basic management of the condition. It includes:
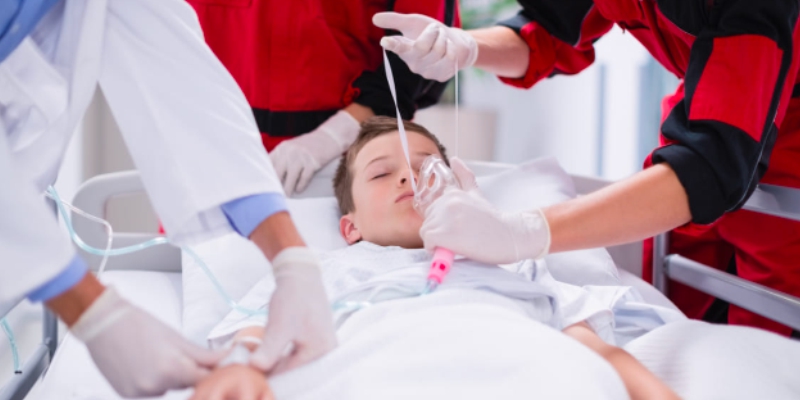
1. Maintain adequate airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs):
An inadequate airway can pose the most critical risk to your child with epilepsy. The best paediatric neurologist in Chandigarh states that hypoxia is the main culprit of complications due to epilepsy in children.
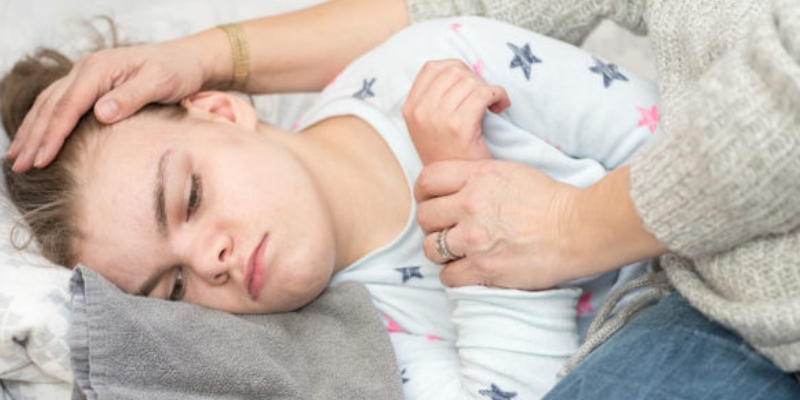
When you notice your child going through an epileptic episode, position them on their side and suction easily accessible secretions. Make sure their mouth is not pried open. After suctioning, reposition them on their back and apply a chin lift to help open the airway. You can also give them oxygen with a face mask.
You may also notice an increased heart rate and blood pressure along with seizures. This, however, is common and returns to normal when the seizures stop.
2. Terminate the seizure and prevent recurrence:
The main goal of the treatment is to stop the seizure and prevent brain injury. In such cases, medications should be administered. Do not, however, self-administer. Consult the best paediatrician & neonatologist in Chandigarh for the use of medications. Your paediatrician will only provide medication for seizures lasting longer than 5 to 10 minutes.
Make sure that you also pay attention to other symptoms. For instance, some children may also have a fever or increased blood pressure. Bring this to the attention of the best paediatric neurologist in Chandigarh.
3. Management of refractory epilepsy:
Epilepsy that is unresponsive to adequate doses of first- and second-line therapies is considered refractory. At this stage, the patient’s care is beyond emergency management, this has to be transferred to the paediatric intensive care unit.
Epilepsy is a common paediatric neurological disorder. Emergency management includes maintaining respiratory stability, immediate administration of appropriate medications at appropriate doses, specific diagnosis and management of potentially life-threatening causes of seizures. Being the parent of a child with epilepsy, you must know which category your child falls into. Make sure that you consult with Dr. Monika Chhajed from the Motherhood Hospitals for accurate management of the condition.
At Motherhood Hospitals, we have a team of experienced specialists backed by the cutting edge facilities. We have the best Paediatric Neurologist in Chandigarh.
Do take an appointment with the best Paediatric Neurologist in Chandigarh at a centre closest to you. Meet with our doctors who will carry out the required investigations, diagnose the issue and recommend the most appropriate treatment, enabling you to lead an active life.
If you wish to get in touch with Dr. Monika Chhajed, please book your appointment here


 Toll Free Number
Toll Free Number